본문
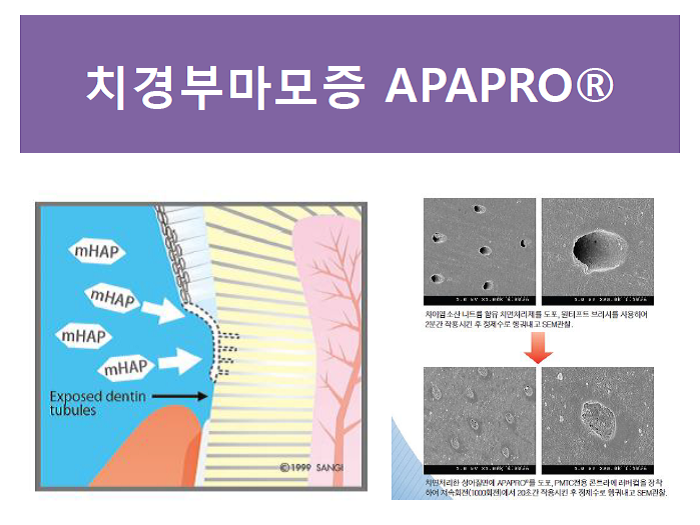
Dentinal tubule
occluding capability of nano-hydroxyapatite; The in-vitro evaluation
. 2018 Aug;81(8):843-854.
Authors
Serdar Baglar 1 , Umit Erdem 2 , Mustafa Dogan 2 , Mustafa Turkoz 3
Affiliations
1 Department of Restorative Dentistry, Faculty of
Dentistry, Kirikkale University, Kirikkale, 71450, Turkey. 2 Scientific and Technological Research Application
and Research Center, Kirikkale University, Kirikkale, 71450, Turkey. 3 Faculty of Engineering, Department of Electric and
Electronics Engineering, Karabük University, Karabuk, 78050, Turkey. Abstract In this in-vitro
study, the effectiveness of experimental pure nano-hydroxyapatite (nHAP) and
1%, 2%, and 3% F¯ doped nano-HAp on dentine tubule occlusion was investigated.
And also, the cytotoxicity of materials used in the experiment was evaluated.
Nano-HAp types were synthesized by the precipitation method. Forty dentin
specimens were randomly divided into five groups of; 1-no treatment (control),
2-specimens treated with 10% pure nano-HAp and 3, 4, 5 specimens treated with
1%, 2%, and 3% F- doped 10% nano-HAp, respectively. To evaluate the
effectiveness of the materials used; pH, FTIR, and scanning electron microscopy
evaluations were performed before and after degredation in simulated body
fluid. To determine cytotoxicity of the materials, MTT assay was performed.
Statistical evaluations were performed with F and t tests. All of the nano-HAp
materials used in this study built up an effective covering layer on the dentin
surfaces even with plugs in tubules. It was found that this layer had also a
resistance to degradation. None of the evaluated nano-HAp types were have
toxicity. Fluoride doping showed a positive effect on physical and chemical
stability until a critical value of 1% F- . The all evaluated nano-HAp
types may be effectively used in dentin hypersensitivity treatment. The formed
nano-HAp layers were seem to resistant to hydrolic deletion. The pure and 1%
F- doped nano-HAp showed the highest biocompatibility thus it was
assessed that pure and 1% F- doped materials may be used as an
active ingredient in dentin hypersensitivity agents. Keywords: cytotoxicity; degredation; dentine hypersensitivity;
dentine tubule occlusion; fluoride; hydroxyapatite.
|
